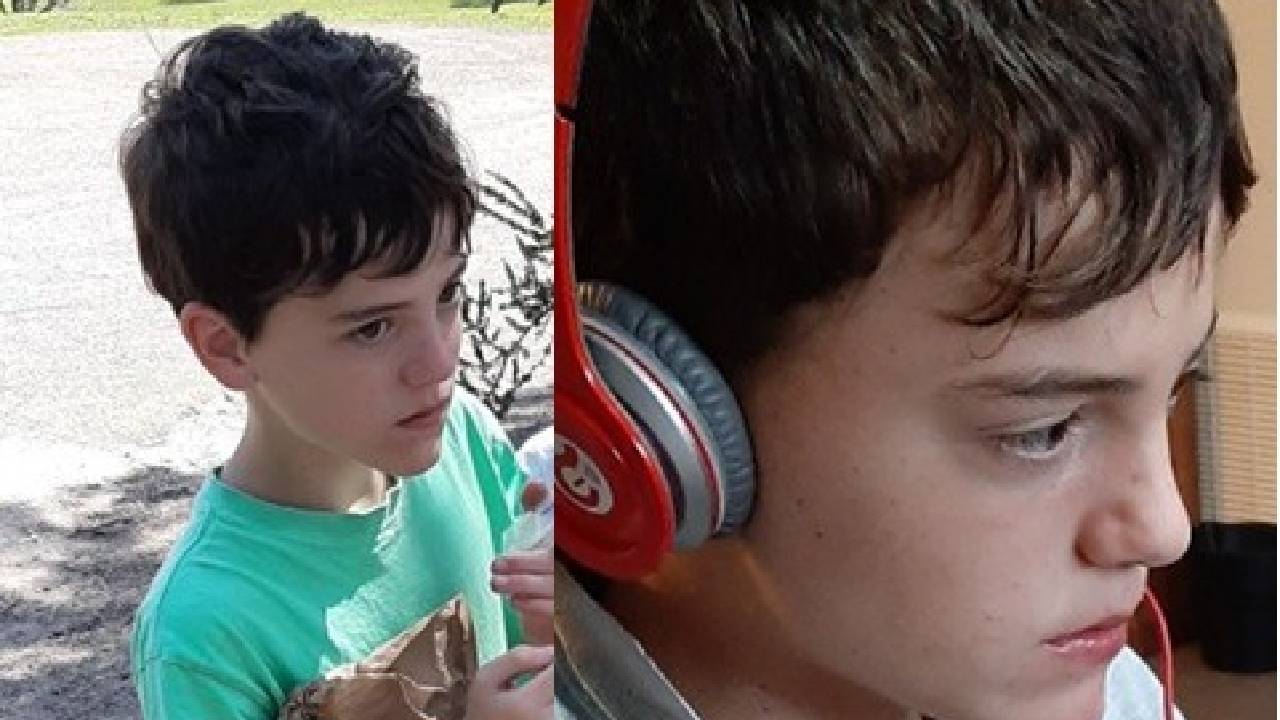
The search for a missing 14-year-old boy with nonverbal autism is continuing Tuesday morning on a Victorian mountain where temperatures dropped to zero degrees Celsius overnight.
About 300 people have joined an air and ground search for William Callaghan, who was last seen on the south side of Mount Disappointment’s summit about 2.20pm on Monday.
Police said Callaghan was not dressed for cold conditions and had no food or water.
“Police have been told William is very energetic. We believe he could cover a lot of distance,” Victoria Police said.
They also warned that Callaghan was “food-focused” and could walk into a house to help himself to the fridge or cupboard. He could also put himself to bed, police said.
Residents in the area are asked to check their bedrooms and outhouses, and contact Triple Zero (000) immediately if they sight Callaghan.
Acting Inspector Christine Lalor said Callaghan taps on his chest to communicate, and anyone who finds the boy should approach him in a calm manner.
The Police Airwing, the Search and Rescue Squad, Dog Squad, local uniform members in 4WD and police on bikes were being supported by the State Emergency Services in their search through Monday night.