The legendary dire wolf – an iconic creature that vanished around 13,000 years ago and gained fame through HBO’s Game of Thrones – has made an extraordinary return. This resurgence is the result of a cutting-edge genetic project spearheaded by Colossal Biosciences, marking the first-ever successful “de-extinction” of a species.
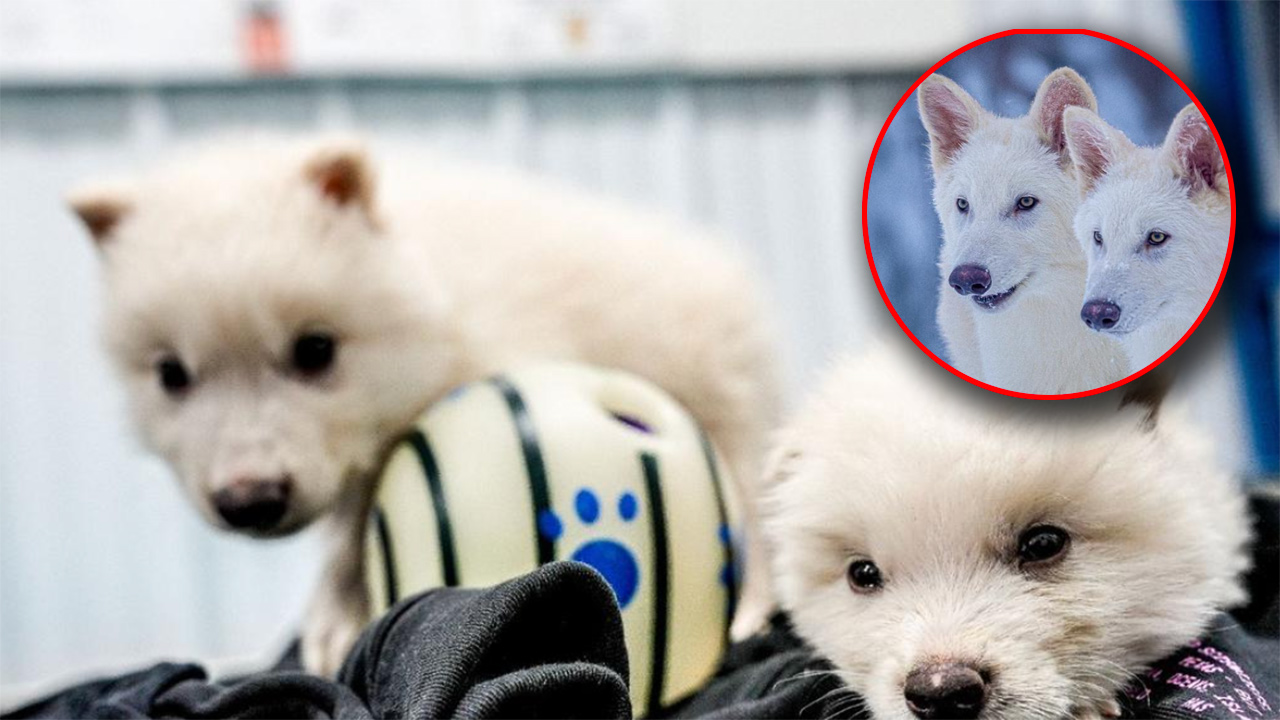
In a groundbreaking announcement recently, Colossal revealed the birth of three healthy dire wolf pups – Romulus, Remus, and Khaleesi – who were created by combining DNA from ancient dire wolf fossils and the genes of their closest living relative, the grey wolf. The news marks a milestone in both genetic engineering and conservation science, offering a glimpse into the future of species revival.
The pups’ arrival was made possible by the expertise of Colossal’s team, which used DNA from a 13,000-year-old tooth and a 72,000-year-old skull. Ben Lamm, CEO of Colossal, expressed his excitement over the breakthrough, saying, “It was once said, ‘any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic’. Today, our team gets to unveil some of the magic they are working on and its broader impact on conservation.”
The dire wolf pups were created using somatic cell nuclear transfer, a cloning technique that involved inserting cell nuclei from the ancient DNA into donor egg cells. These embryos were then implanted into a surrogate dog mother, who gave birth in January.
The pups are now thriving in a secure 800-hectare ecological preserve, where they receive round-the-clock care from a dedicated team of 10 staff members.
The dire wolf, once a dominant predator across North America, were fierce hunters that roamed alongside Ice Age megafauna such as mastodons and sabre-toothed tigers. They preyed on large mammals like horses, bison and potentially mammoths, but after these species went extinct, the dire wolf’s reign also came to an end. According to palaeontologist Julie Meachen, with the loss of their prey, the dire wolf was gradually replaced by the grey wolf, which filled the ecological void.
Dire wolves were notably larger and more muscular than their modern grey relatives, with jaws and shoulders built for powerful hunts. Their revival has captivated both science enthusiasts and pop culture fans alike.
Lamm and George Church, a Harvard biologist, co-founded Colossal Biosciences with the ambitious goal of bringing back extinct species. The company is also working toward reviving the woolly mammoth and the Tasmanian tiger, and has already successfully engineered a woolly mouse, known for its curly fur reminiscent of the woolly mammoth’s iconic coat.
Dr Christopher Mason, a scientific adviser for Colossal, hailed the de-extinction of the dire wolf as a transformative leap in genetic engineering. “This is an extraordinary technological leap for both science and conservation,” he stated. “It’s a wonderful example of the power of biotechnology to protect species, both extant and extinct.”
Images: Colossal Biosciences